CBD-Aloe Vera Combination Shows Promise in Human Tissue Tests
Initial research with live human tissue suggests that a CBD-Aloe Vera (Hemp) formulation developed by Desert Harvest may decrease the activity of pain receptors—which could lead to new approaches to treating chronic pain, including interstitial cystitis (IC)/bladder pain syndrome (BPS).
New Evidence for CBD-Aloe Vera and Chronic Pain
The research on the role of the cannabinoids found in marijuana in treating chronic pain is part of an ongoing partnership between Desert Harvest and Dr. Reza Sharif Naeini of the McGill University Research Center for Cannabis. The newest findings, released in July, were based on a study conducted by Canadian researchers on human tissue from organ donors.
Researchers found that a formulation of the non-psychoactive chemical cannabidiol (CBD) and Aloe Vera developed by Desert Harvest dampened the response of neurons called dorsal root ganglion (DNG) play a primary role in relaying sensory information to the nervous system and brain. The results suggest the formulation may dampen so-called “nociceptive excitability” compared to a control group, “demonstrating an effect potentially relevant to chronic pain treatment,” researchers observed.
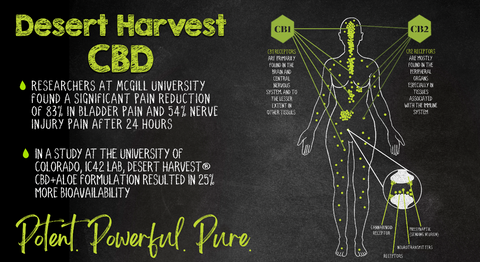
The new findings are the first to involve human tissue. They follow an earlier preclinical trial in which mice were injected with chemicals to test the effect of the CBD-Aloe Vera formulation on symptoms similar to human IC/BPS, including bladder inflammation, pain, and bladder overactivity. In that research, the Desert Harvest CBD-Aloe Vera formulation led to statistically significant pain reduction among the treatment group—28% lower four hours after injury pain, 83% lower 24 hours post-injury, and 35% lower at 48 hours. Researchers also found significant pain reductions in a mouse model of neuropathy and chemotherapy pain but no significant changes in a mouse model of osteoarthritis. Additional research to be conducted by Dr. Jason McDougall at Dalhousie University in Nova Scotia will repeat the osteoarthritis model and evaluate and the impact of the formulation in a mouse rheumatoid arthritis model.
Aloe Vera and IC/BPS
Previous clinical trials conducted for more than a quarter-century have confirmed that Aloe Vera helps relieve IC/BPS symptoms such as pelvic pain, urethral burning, and urgency and frequency of urination in many patients. The more recent research involving the CBD-Aloe Vera formulation suggests it “should be explored as an emerging strategy to manage chronic pain,” the researchers stated in their findings (see the poster below). As research continues, Desert Harvest will explore additional women's health pain models with Dr. Sharif-Naeini at McGill, including potential models of menstrual pain, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
The use of CBD to treat chronic pain conditions continues to grow. Click here for some background and medical news about CBD and CBD-Aloe Vera.
What is CBD?

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a chemical found in marijuana. It is one of over 80 chemicals known as cannabinoids found in the Cannabis sativa plant. CBD is obtained from hemp, a form of the Cannabis sativa plant that only contains small amounts of tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, the active ingredient in marijuana that produces a high.
CBD products are often marketed as CBD or hemp oil, but CBD is also sold as an extract, vaporized liquid, CBD capsules, creams, or other CBD topicals which can be applied to the skin. CBD is also added to food and drinks. In Australia, CBD has been approved to treat chronic pain, muscle spasticity from multiple sclerosis and cancer pain.
Although CBD is generally well tolerated, possible complications include dry mouth, diarrhea, reduced appetite, drowsiness, and fatigue. CBD can also interact with other medications, including blood thinners.
Is Cannabidiol or CBD legal?
Since 2017, it’s been legal to sell hemp and hemp products nationwide in Australia with THC quantities below 1%. Hemp oil and CBD products don’t contain tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive ingredient found in marijuana that produces a high.
As a Harvard Medical School fact sheet notes, hemp is legal nationwide, and as a result, banning CBD “would be like making oranges legal, but keeping orange juice illegal.”
What are the different types of CBD?
There are three different types of CBD, each of which includes various parts of the cannabis plant and the cannabinoids found in it.
- Full-spectrum CBD includes all parts of the cannabis plant but contains less than 0.3 percent of THC, the psychoactive component in marijuana.
- Broad spectrum CBD contains most compounds in the cannabis plant, including trace amounts of THC.
- Isolates only contain CBD, with no other cannabinoids or THC.
Research suggests that full spectrum CBD and broad spectrum CBD produce responses in the people who take them, partly because of the “entourage effect”—when a combination of compounds work together in ways that may not be fully understood.
The quality of CBD products also varies, regardless of the type of CBD or active ingredients. A recent study of 84 CBD online products showed that more than a quarter contained less CBD than what was stated on product labels. Other questions have been raised about bioavailability—the body’s ability to absorb the cannabidiol when ingested in the form of CBD capsules. But a research study conducted at the University of Colorado’s iC42 bioanalytical service center found that Desert Harvest’s CBD-Aloe Vera formulation resulted in 25 percent greater bioavailability of CBD and metabolites in blood samples after two hours.
Can CBD reduce chronic pain?
CBD and CBD products do not cure any disease or condition, but numerous studies suggest that CBD could help lower pain and inflammation. The most significant barrier to a more vital link between CBD and chronic pain is that much of the research has involved animal models, including the first phase of the McGill University Research Center for Cannabis study of the Desert Harvest Aloe Vera-CBD formulation, which involved a rodent model. That’s one of the reasons the second phase of the research described in this post—the first test involving human tissue—is so promising.
What is the connection between Aloe Vera and CBD?
Like the cannabis plant, Aloe Vera has more than 200 ingredients. Previous clinical trials conducted for more than a quarter-century have confirmed that Aloe Vera helps relieve IC/BPS symptoms such as pelvic pain, urethral burning, and urgency and frequency of urination in many patients.
Desert Harvest Aloe Vera products are unique in that the high concentration of nutrients in our Super-Strength Aloe Vera preserves the glycosaminoglycans (GAG), which adhere to the bladder mucosal lining, preventing potentially irritating solutes in the urine from reaching the bladder wall. Desert Harvest Super-Strength Aloe Vera naturally coats the bladder with a protective GAG layer without harsh chemicals or side effects.
Ongoing research on CBD-Aloe Vera has shown considerable promise in treating many chronic pain conditions, including IC/BPS, neuropathy, and chemotherapy pain.






